Overview
Single Sign-On (aka SSO) is an authentication process that allows a user to access multiple applications with only one set of credentials.
Single Sign-On is a common practice around corporations that handles lots of users and lots of applications.
Common SAML terms
Understanding how SAML-based Single Sign-On works can be a complicated task as it introduces terms that can be obscure at first glance.
IDENTITY PROVIDER (IDP)
The Identity Provider is the authority that verifies the user's identity and grant access to a requested application (aka the Service Provider)
SERVICE PROVIDER (SP)
The Service Provider is the hosted resource that the user tries to access. In our scenario, the SP is a part of the PIM that handles the authentication process.
ENTITY ID
An Entity ID is a globally unique name for an Identity Provider or a Service Provider. This unique name is used to identify each parties in the SSO process. For the Service Provider, the Entity ID is automatically generated and corresponds by default to the metadata URL of the SP.
ASSERTION CONSUMER SERVICE (ACS)
The ACS is the SP endpoint (URL) that is responsible for receiving the SAML response from the IdP.
METADATA
Metadata is a set of information supplied either by the IdP or the SP, in XML format.
-
Service Provider: The metadata information provided by the SP contains the Entity ID, the X.509 certificate used for decrypting messages coming from the SP, the Logout URL and the ACS URL.
The SP metadata information can be accessed at the following URL: https://YOUR_PIM_SERVER/saml/metadata. Depending on your IdP, this metadata URL can be directly imported into the IdP to ease the configuration process.
- Identity Provider: The IdP can also supply metadata to help configure the SAML communication. At this time, it is not possible to import it in the PIM to configure the Single Sign-On.
What is SAML?
SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) is an XML-based standard for exchanging authentication data between an Identity Provider (IdP) (such as Microsoft Azure AD) and a Service Provider (SP) (in our case our beloved PIM).
Configure the SSO
SAML-based Single Sign-On is a two-way communication between an authentication server (the Identity Provider) and an application (the Service Provider). Therefore, your PIM needs to be configured to declare who will be the authentication server and how the communication must work.
Gather information from your Identity Provider (IdP)
First of all, before configuring your PIM to communicate with an Identity Provider, you will have to gather some information about your IdP. Your IT department/SSO administrator must probably have all the information.
Activate the Single Sign-On feature
To activate the Single Sign-On feature, just click on the SSO enabled button in the interface. Once enabled, all the authentication requests will be redirected to the authentication server you specified.
Configure the Identity Provider (IdP) section
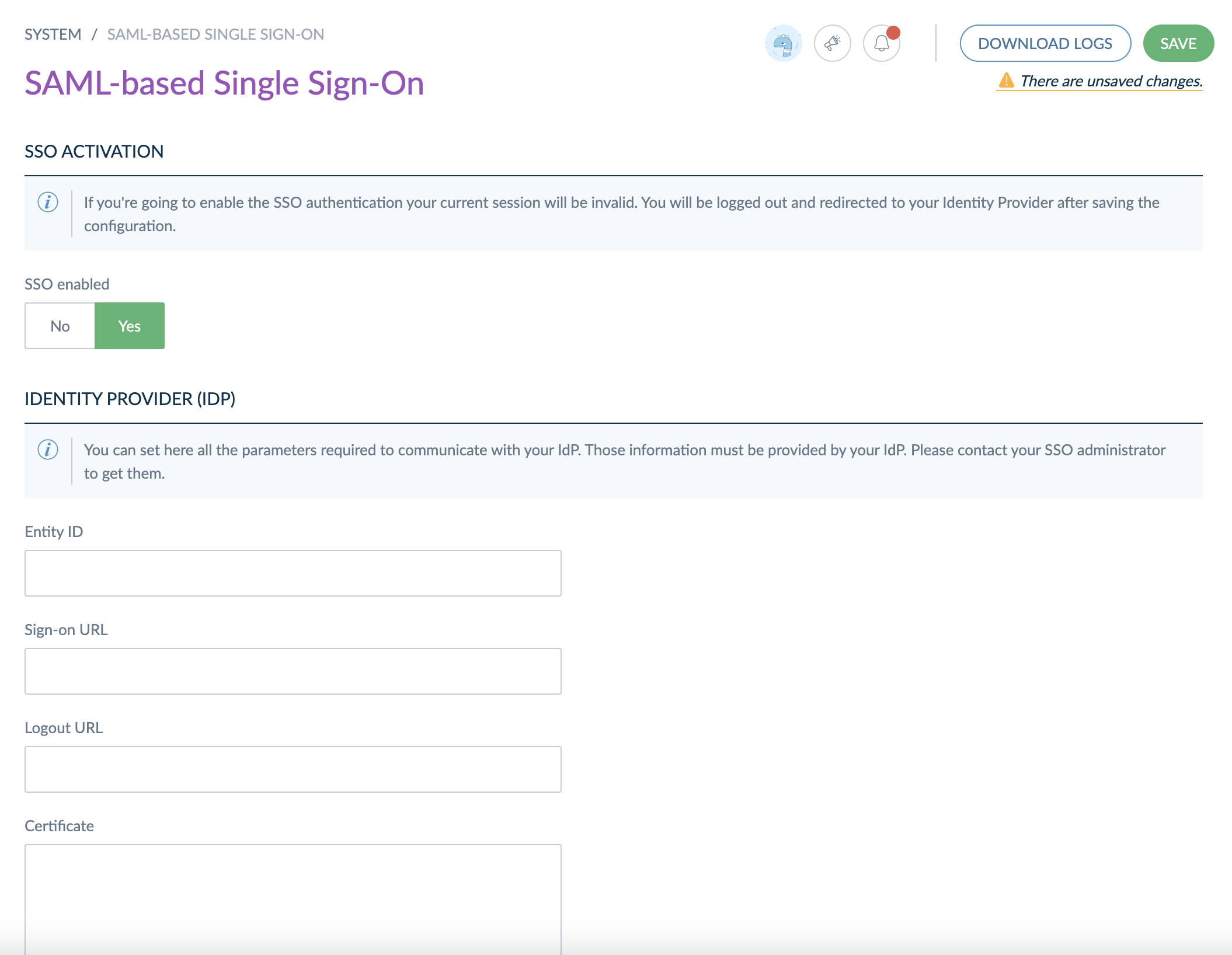
Using the information you gathered previously, you can fill all the required fields that are required to communicate with the IdP. The mandatory values are the following:
- Entity ID: String that uniquely identify your IdP (it is in general provided by your IdP)
- Sign-on URL: URL that will be used when a user tries to log in the PIM
- Logout URL: URL that will be used when a user ask for logout action in the PIM
- Public certificate: As the communications are encrypted between the SP and the IdP, the IdP public key is required in order to decrypt any incoming message.
Certificates must be in X.509 format. For more information about X.509 certificate, you can have a look at this article.
Configure the Service Provider (SP) section
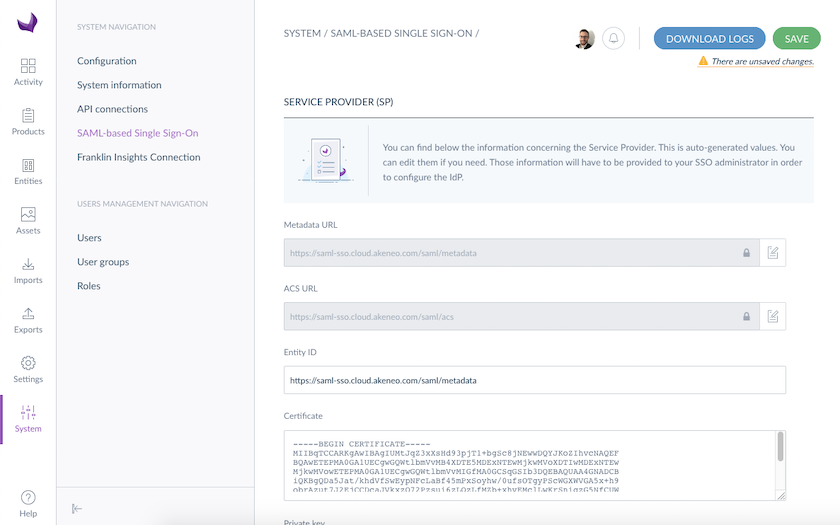
By default, the SP configuration is automatically populated during the first access to the SSO configuration page. If you want to provide your own certificate, you can paste the public and private key certificates in the corresponding fields. These information will be needed to configure your IdP.
The information required for configuring the SP are the following:
- Entity ID: String that uniquely identify your SP (this information needs to be provided to the IdP)
- Public and Private key certificates: As the communications are encrypted, the private and public keys are required to encrypt outgoing messages.
The Metadata URL and ACS URL are read-only. They have a built-in 'copy' functionality to easily copy the URL in the clipboard.
The SP certificate is self-signed by default. The expiration date is visible from the UI. Once expired, you will have to renew it.
Disable the SSO
To disable the Single Sign-On feature, just click on the SSO enabled button in the interface. Once disabled, all the authentication requests will go through the classical login interface.
Tips and tricks
About users in the PIM
Once the SSO will be activated, the passwords that exists on the PIM will no longer be used. On the other hand, the users created in the PIM will still be needed to make the connection between the users coming from the IdP and the user rights existing in the PIM.
You will have to make sure that all the potential users in your IdP that can access the PIM have an account configured in the PIM. Unknown users are not generated on-the-fly when accessing the PIM. If a user doesn't exist in the PIM, he will not be able to access the PIM and an error will be raised.
About user claims
User claims are information that the Service Provider expects when a authentication is made on the IdP and the positive response comes back to the PIM. These values are mandatory for the Single Sign-On in the PIM to work. Your SSO administrator must configure the IdP response to embed these values. Please refer to your IdP's documentation on how to configure claims on the IdP.
The IdP response must contain the following attributes:
- akeneo_uid: Will be used to check the username in the PIM database. This is the most important part of the SAML communication.
- http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/05/identity/claims/surname: Last name of the user
- http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/05/identity/claims/givenname: First name of the user
- http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/05/identity/claims/emailaddress: Email of the user
About security
By design, in order to have the most secure process, all communications between the Identity Provider and the Service Provider have to be encrypted.
Moreover, as far as security is involved, it is mandatory to use the HTTPS protocol around the PIM. Using HTTP communication may be a serious security breach.

